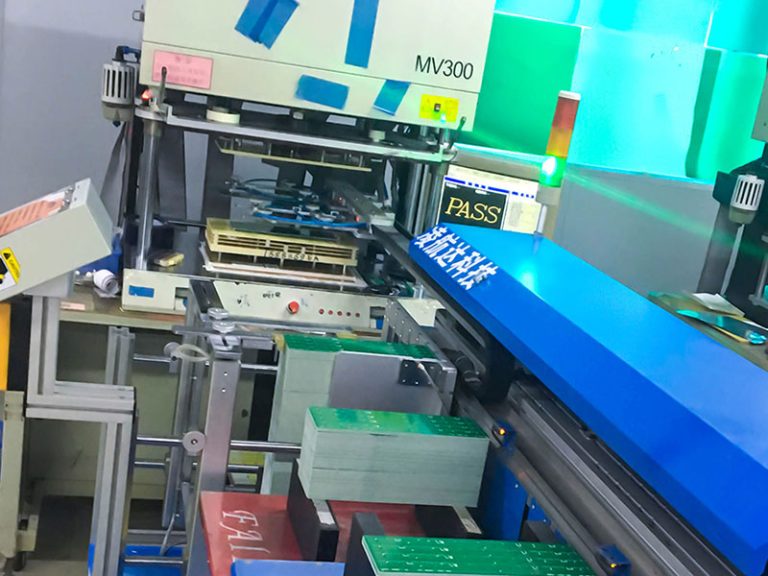
Metal — based copper — clad foil heat dissipation
In the design of printed circuit board with metal substrate as the substrate, not only heat dissipation, but also insulation and reliability should be considered. This is the relationship between the copper foil conductor circuit on different substrates and the fuse current. Metal substrate heat dissipation, fuze current has been significantly increased. The heat dissipation of the metal substrate depends on the thickness of the insulation layer, the thermal conductivity and the type of metal in the substrate.
Mechanical properties of
Metal substrate has high mechanical strength and toughness. The metal substrate also has high dimensional stability and smoothness and can be assembled and processed on substrates that require hammering and riveting. On printed circuit boards with metal substrates, non-wiring components can also be bent and twisted. Some components in electronic products need to prevent electromagnetic radiation. Metal substrate can shield electromagnetic waves.
Thermal expansion
Due to the problem of thermal expansion of rigid resin clad copper foil, especially in the thickness direction, the quality of metallized holes is affected. The main reason is that the thermal expansion direction of material thickness is different and the difference between them is too big. After heating, the expansion of the matrix changes, leading to the fracture or destruction of the copper line and the copper metallized hole. Compared with common resin clad copper foil, its thermal expansion coefficient is closer to that of copper, which is beneficial to the quality and reliability of metallized holes.


-768x513.jpg)

-768x576.jpg)

