Table of Contents
ToggleAn electronic component is also known as an electrically controlled device. Electronic components are designed to perform various electrical operations and are available in different shapes and sizes. This article is about features related to electronic components and the assembly of electronic components.
Features of electronic components
- Passive and active components
Passive components include resistors, memristors, capacitors, and inductors. These components don’t provide power amplification or any signal gain. Ideally, it multiplies an incoming signal with values less than one.
Ideally, it performs switching action by interpreting and amplifying signals in multiple ways. On the other hand, active components manipulate input signals by controlling current and voltage levels. Active components include diodes, transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and silicon-controlled rectifiers. Active components comprise semiconductor devices and can gain more than one.
- Embedded Components
PCB manufacturers are using embedded components for producing consumer electronics. Mostly the ICs and passive components are embedded. We can integrate embedded components into wearable devices while the production loads and development costs get minimized.
Embedding passive components makes it easy to embed every available part. Thinner boards are feasible because of embedding the advanced thin passive components. The resin closes these thin Components and embeds them while board layers are assembled. So, there will be no need to make holes in the board.
The packaging stage gets amplified by printing film components, thus reducing assembly of electronic components cost as film components are in batches. As solder joints decrease, the complexity of the circuits also reduces; thus, a compact product improves joint durability and has a less environmental impact.
- Discrete and Integrated Components
A discrete component is an individual component that operates independently within a circuit. A capacitor is a suitable example as its purpose is to store charge when the current goes through it. Discrete components can be active or passive devices.
Integrated circuits, on the other hand, are created when various discrete components get combined, interconnected, and packaged in a special enclosure to perform specific functions. Microprocessors, FPGAs, and microcontrollers are perfect examples.
Connection types of components
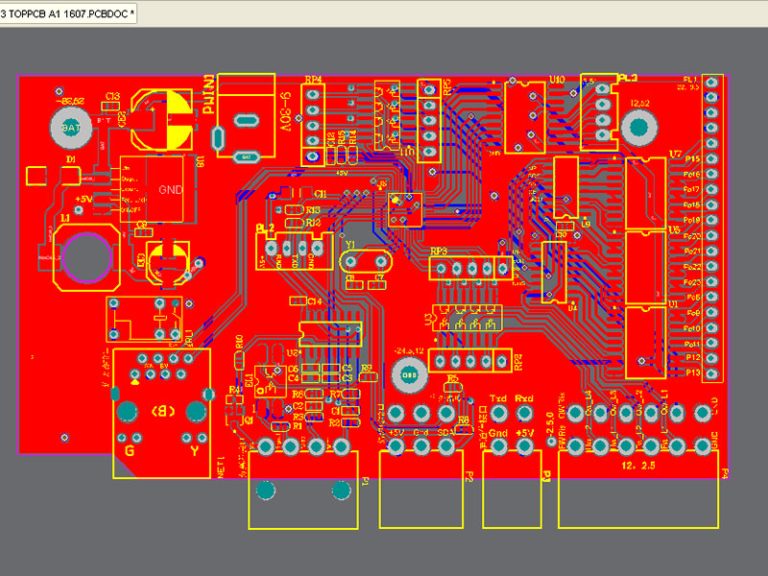
Electronic components can be connected to the PCB board using Surface mount (SM) components or Through-hole (TH) components. SM components are placed directly on the PCB surface, whereas TH components contain leads inserted in the drilled holes in the board.
During the assembly of electronic components, SM components are preferred for use in high-density IC assemblies available in many pin-grid arrays located at the bottom of the components.
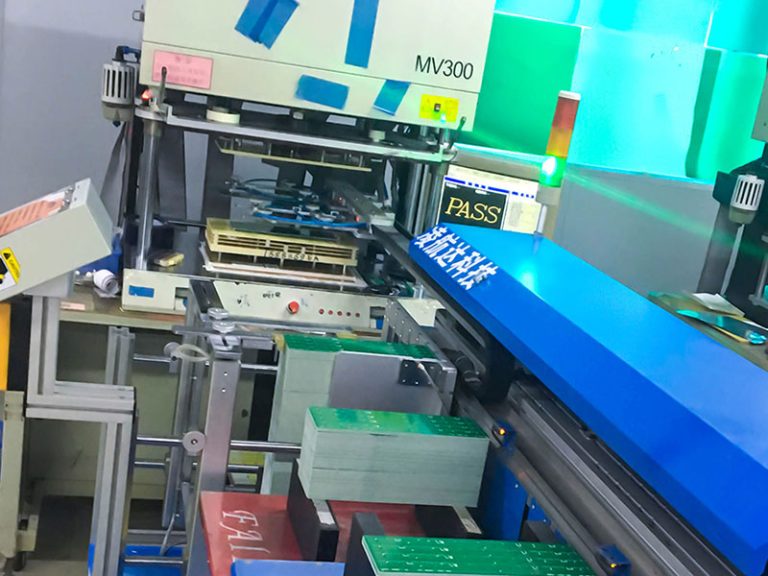
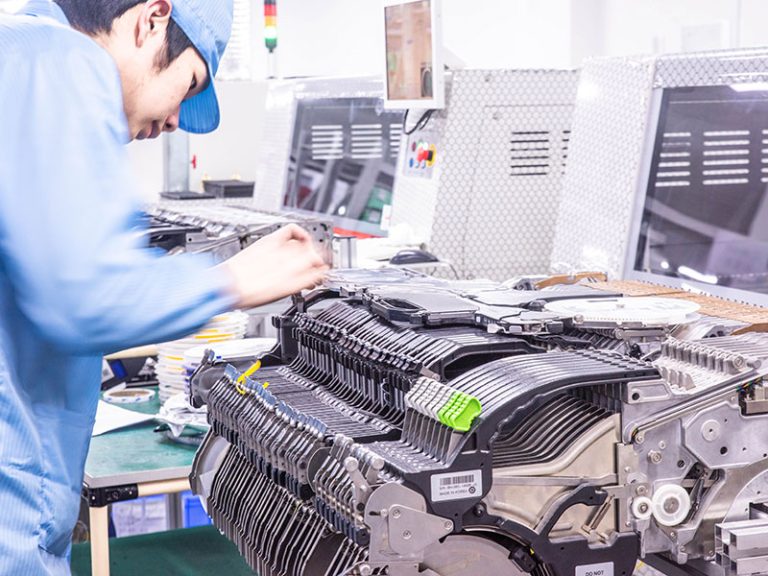
Assembly of electronic components process
The assembly of electronic components process includes subsequent phases. However, the process entirely depends on the Manufacturers capabilities. It includes;
- Collecting components according to the BOM requirements
- Getting components ready for placement
- Cleaning PCB by either rinsing in water using industrial cleaners or wiping
- Recording boards and components measurements
- Placing components in separate plates in an automated assembly line
- Insertion of PTH devices and placement of SMT device
- Mass soldering such as reflow soldering
- Cleaning and removal of flux
- Placement of sensitive or heavy components
- Manual soldering
- Cleaning residual materials
- Inspection and testing
- Application of finish and conformal coatings
- Storage and warehousing
At LHD Technology, we are equipped with all the necessary equipment for the best assembly of electronic components process. You can count on our one-stop service for all your needs.


-768x513.jpg)

-768x576.jpg)

